|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Ripe Malis"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | HIP 41378 e |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 0.038 |
| Radius | 0.437 |
| Orbital period | 131 |
| Discovered | 2016 |
| Updated | 2025-02-10 |
| Tzero tr | 2457140 |
| Impact parameter | 0.31 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Primary Transit |
| Mass measurement type | Radial Velocity |
| Radius measurement type | Primary Transit |
| Star name | HIP 41378 |
| Right ascension | 126.62° |
| Declination | 10.08° |
| Mag v | 8.9 |
| Star distance | 116 |
| Star metallicity | 0.046 |
| Star mass | 1.245 |
| Star radius | 1.306 |
| Star sp type | F7V |
| Star age | 1.8 |
| Star temperature | 6199 |
| Star alternate names | K2-93 |
| Wikipedia article | HIP 41378 e |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Ripe Malis |
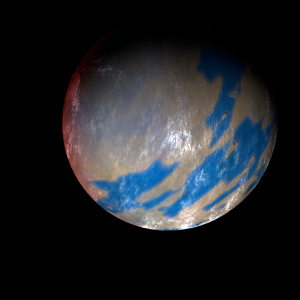
| Planet type | Small cold gas planet |
| Its orbital period around HIP 41378 of 130 earth days is the longest of all the planets in its solar system.
A prominent result is the "great blue spot", a giant storm that is known to have existed for centuries since it was first detected by scanner. |
| Atmosphere | Argon | 53% |
| Hydrogen deuteride (HD) | 16% |
| Nitrogen | 16% |
| Ozone | 7.4% |
| Ammonium hydrosulfide (NH4SH) | 5.2% |
| Methane | 1.3% |
| Formaldehyde | 0.6% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 4 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Ripe malis |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|