|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Enang"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | HIP 19976 c |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 30.609 |
| Orbital period | 17128.4 |
| Semi major axis | 11.522 |
| Orbit eccentricity | 0.406 |
| Inclination | 60.988 |
| Discovered | 2022 |
| Updated | 2024-06-15 |
| Omega | 90.414 |
| K | 293.994 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Radial Velocity, Primary Transit |
| Mass measurement type | Astrometry |
| Star name | HIP 19976 |
| Right ascension | 64.26° |
| Declination | -40.8° |
| Mag v | 10.4 |
| Mag i | 8.98 |
| Mag j | 8.109 |
| Mag h | 7.55 |
| Mag k | 7.381 |
| Star distance | 40.2707 |
| Star mass | 0.67 |
| Star radius | 0.772 |
| Star sp type | K7V |
| Star temperature | 4316 |
| Star alternate names | GJ 9152, L 374-19 |
| Wikipedia article | HIP 19976 c |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
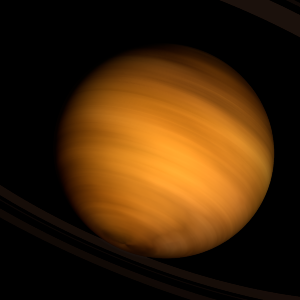
| Suggested name | Enang |
| Planet type | Huge cold gas giant |
| The polar regions are constantly below 315°K (42°C).
Its north and south poles, therefore, lie where most other planets have their equators. Wind speeds can reach 158 metres per second. |
| Atmosphere | Ethane | 57% |
| Carbon dioxide | 34% |
| Carbonyl sulfide | 7% |
| Hydrogen | 1.2% |
| 2H2O | 0.0027% |
| Oxygen | 0.0015% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 5 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Enang |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|