|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Nycokan"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | HD 104289 b |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 49.483 |
| Orbital period | 1233.33 |
| Semi major axis | 2.42 |
| Orbit eccentricity | 0.377 |
| Inclination | 117.28 |
| Discovered | 2023 |
| Updated | 2024-06-30 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Astrometry |
| Mass measurement type | Astrometry |
| Star name | HD 104289 |
| Right ascension | 180.17° |
| Declination | 59.35° |
| Mag v | 8.07 |
| Mag j | 7.048 |
| Mag h | 6.887 |
| Mag k | 6.783 |
| Star distance | 70.369 |
| Star mass | 1.213 |
| Star radius | 1.404 |
| Star sp type | F8IV-V |
| Star temperature | 6108.74 |
| Wikipedia article | HD 104289 b |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Nycokan |
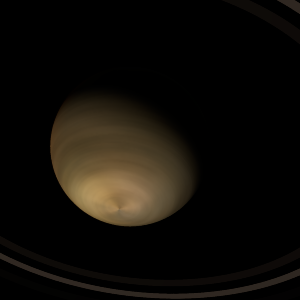
| Planet type | Huge cold gas giant |
| It has the longest rotation period (445 days) of any planet in its solar system and rotates in the opposite direction to most other planets.
A prominent result is the "great green spot", a giant storm that is known to have existed for centuries since it was first detected by scanner. |
| Atmosphere | Hydrogen deuteride (HD) | 33% |
| Nitrogen | 31% |
| Hydrogen | 25% |
| Ozone | 11% |
| Carbonyl sulfide | 0.28% |
| Water vapor | 0.00045% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 20 bar |
 |
| Moon | Esakon | Small irregular crater-filled asteroid |
| Yquw | Small almost round rocky moon |
| Google search for Nycokan |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|